Optical Enhancement in Periodic Plasmonic Gratings for SERS and Metal-Semiconductor-Metal Photodetectors (MSM-PDs) applications
Student: Ahmad A. Darweesh
Degree: Ph.D., May 2019
Major Professor: Dr. Joseph B. Herzog
Research Area(s):
Microelectronics
Photonics
Background/Relevance
- Free electrons in metallic structures receiving an incident electric field have been shown to exhibit collective oscillations and produce increased electromagnetic fields (i.e. plasmons).
- Deposition of metallic nanostructures on a semiconducting substrate allow for generation of greater photocurrent in the device.
Innovation
-
Enhanced structure design and accurate nanofabrication techniques will lead to greatly improved photovoltaic and photo-detection applications.
Approach
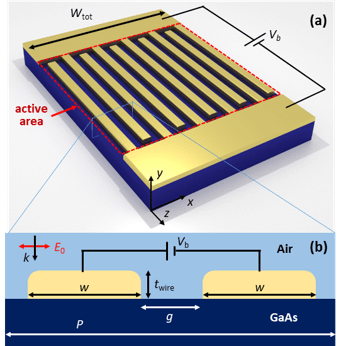
- Generate air/GaAs models in COMSOL FEM software for nano-scale devices.
- Develop script in MATLAB to calculate and plot optical enhancement given raw data from COMSOL.
- Perform various parametric sweeps to vary structural aspects of the structure.
Key Results
- Demonstrated computationally that a reduction in the gap between structures will generate an increase in optical enhancement due to plasmonic effects.
-
Determining a weighted relationship between the optical enhancement and current density.
Conclusions
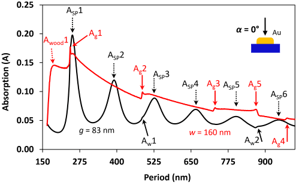
- Smaller nano-gap (g) between structures increases the optical enhancement produced.
- Period as a function to gap space can give sharper absorption spectrum.
- Smaller wire width (w) and gap space (g) generate more current density