Investigation of CNT-Induced E. coli lysis and Protein Secretion
Student: Abdollah Mosleh
Degree: M.S., August 2016
Major Professor: Dr. Bob Beitle Jr.
Research Area(s):
Nanoscience & Engineering
Biological Materials & Processes
Background/Relevance
- Extracting proteins from periplasm and cytoplasm are always an issue in bioengineering.
- Carbon nanotubes are capable to make E. coli leaky
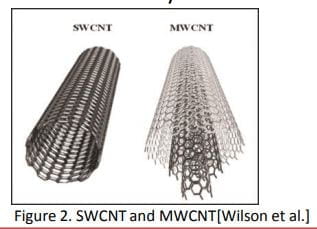
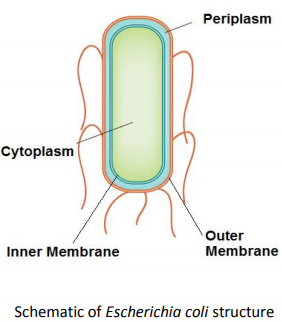
Approach
- Disperse functionalized CNTs in aqueous medium.
- Add CNTs solution to the flask containing cell pellets and Tris base.
- Take samples using installed syringe then centrifuged them for separation of proteins from dead cells.
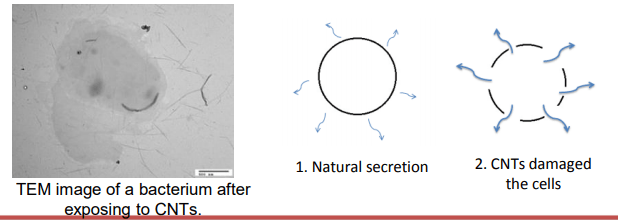
Key Results
- By increasing the amount of CNTs, the amount of secretion will increase.
- By increasing the agitation rate, more materials will be secreted to the medium.
- CNTs will damage the cell walls and cause the leakage of periplasmic materials
- CNTs could damage the cytoplasm and they may cause its material to leak out to the medium.
- It was shown that CNTs can lyse the cells close the lysozyme treatment
Conclusions
- CNTs damaged the cell walls and the periplasmic and cytoplasmic materials leaked out to the medium
- High agitation rate (around 600 rpm) played an important role in destroying the cells.
- It was indicated that CNTs can lyse the cells up to 90% of lysozyme treatment.
- By increasing the amount of CNTs, the amount of secretion has increased.
- By increasing the agitation rate, the amount of secretion has increased.
