Design of Asynchronous Polymorphic Logic Gates
Student: Chandler Bernard
Degree: M.S., May 2020
Major Professors: Dr. Jia Di
Research Area(s):
Microelectronics, Modeling and Simulation
Background/Relevance
- Polymorphic circuits, or circuits with two superimposed functionalities triggered by a change in supply voltage, have applications in hardware security and cryptography.
- Asynchronous MTNCL serves as an ideal logic paradigm for such circuits due to its handshaking signals preventing a latched unstable output during function change.
Innovation
- Design of the first asynchronous polymorphic logic gate set
- Design of the first asynchronous polymorphic combinational logic circuit
Approach
- Design and simulate using Cadence software suite.
- Use TSMC 90nm process.
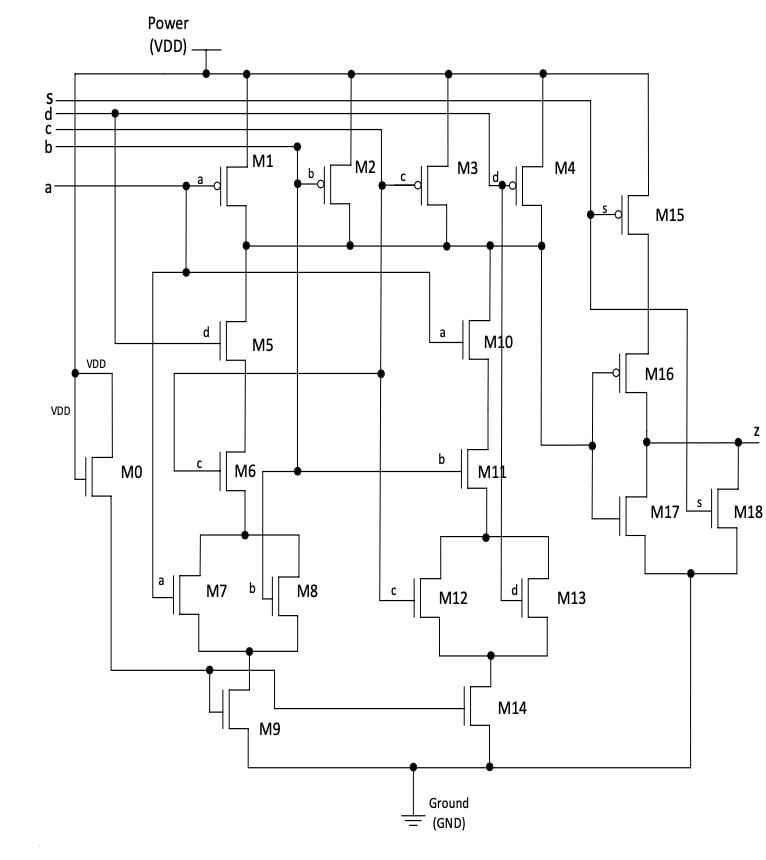
- Design methodology includes selective gating using a threshold drop NMOS.
- At low supply voltage, the voltage drop across the NMOS will be more significant than at high voltage, possibly pushing the gating transistor closer to linear or cutoff region operation.
- Selective gating is used to achieve dual-functionality.
Key Results
- The first polymorphic logic gate set was designed, with all MTNCL functional combinations possible using various circuit gating techniques.
- Undesirable portions of logic gates are throttled with a threshold drop NMOS transistor serving as a selective resistor, allowing correct and stable output at each supply voltage.
- An MTNCL Multiplier-RCA was designed, functioning as a multiplier at the higher supply voltage, and an RCA at the low supply voltage.
Conclusions
- There is a significant active power tradeoff for implementation of MTNCL polymorphic gates that varies in severity by process node.
- Polymorphic gates can be much smaller in area than the combination of two individual MTNCL gates with comparable leakage power.
Future Work
- Larger MTNCL polymorphic combinational logic circuits will be designed with hardware security in mind.
