Graphene Oxide Based Nonflammable, Temperature Stable Proton-Conducting Membranes
Student: Hulusi Turgut
Degree: Ph.D., August 2016
Major Professor: Dr. Ryan Tian
Research Area(s):
Conventional Materials & Processes
Nanoscience & Engineering
Background/Relevance
- Current proton conductive membranes are not operable at higher temperatures which is not desirable.
- Graphene oxide’s high flammability may bring a great deal of fire hazard to manufacturers and consumers.
Innovation
- Use modified graphene oxide (GO)- polybenzimidazole (PBI) composites to develop non-flammable, temperature stable, proton conductive membranes.
Approach
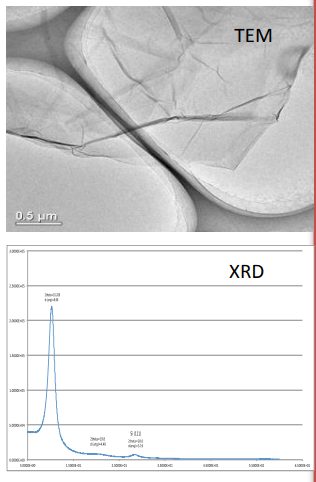
- GO is synthesized by using modified Hummer’s method.
- PBI is dissolved in dimethylacetamide (DMAc)
- Composite membranes were obtained by drop casting method at 60 °C.


Key Results
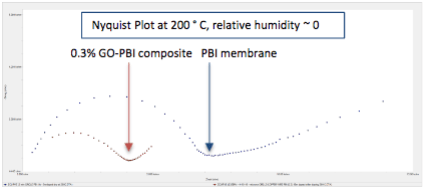
- 0.3% GO-COOH added polybenzimidazole (PBI) fuel cell membranes exhibited much lower resistance at 200 °C compare to polybenzimidazole membranes.
Conclusions
- Industry viable, temperature stable GO-PBI membranes were casted.
- The resulting membranes exhibited enhanced thermal stability.
- GO addition significantly increased proton conductivity.
Future Work
- Various approaches will be applied to develop cost-efficient fuel cell stack.
- GO is modified to enhance efficiency of fuel cell stack
