Theoretical Study of 2D Materials Using Zone Folding Approximation
Student: Jaylan Dawson
Major Professor: Dr. Salvador Barraza-Lopez
Research Area(s):
Modeling & Simulation
Background/Relevance
- Zone folding approximation is a method used to make predictions on the band structure of unit cells.
- Thanks to our capabilities to create small devices, the processing power of chips are gradually increasing, but the materials that can be used is limited.
Innovation
- Use time-independent Schrödinger’s Equation and Bloch’s Theorem in conjunction with tight binding calculations.
Approach
- Use the zone folding approximation with 1D chain.
- Predict the band structure of a 1D chain with a 1 atom unit cell.
- Predict the band structure of a 1D chain with a 2 atom unit cell.
- Calculate new eigenvalues to unfold the band structure of 2 atom unit cell.
- Changing from a reduced to extended brillouin zone
Key Results
- Successful in creating graphs for the band structure of the unit cells
- Successful in simulating the band structure of reduced brillouin zone from the diatomic unit cell
- K-values in one brillouin zone share the same eigenvalue with other k-values in other brillouin zones.
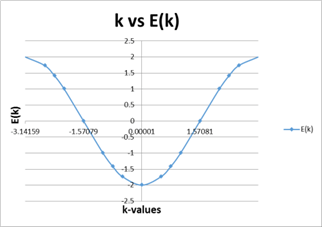
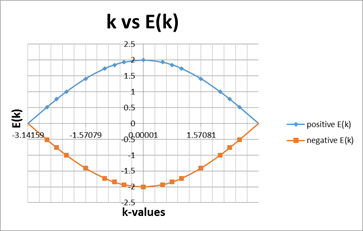
Conclusions
- Can be used for optical lattices, supercells with defects, and a multitude of other uses.
- It can be used for material adaptation.
