Measure Nonlinearity Parameters of Graphene Via Z-Scan
Student: Thekrayat AlAbdulaal
Degree: Ph.D., December 2016
Major Professor: Dr. Gregory J. Salamo
Research Area(s):
Nanoscience & Engineering
Background/Relevance
- Nonlinear optical (NLO) properties play significant roles in optical communication and other optical signal applications.
- Graphene has illustrated excellent NLO properties, including reverse saturable absorption, two-photon absorption, four-wave mixing, and saturable absorbers.
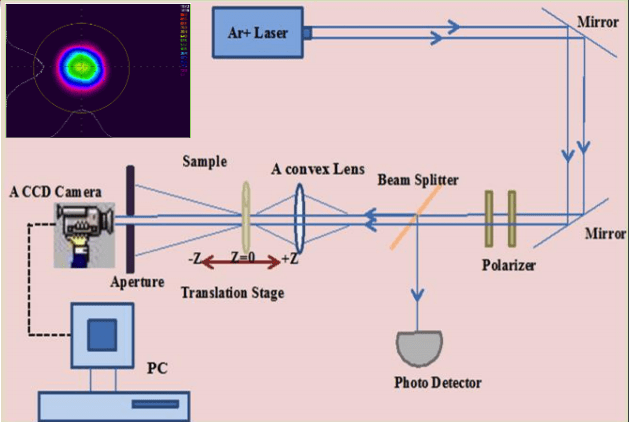
- Z-Scan is a standard technique to define the sign and the magnitude of nonlinear properties due to its setup simplicity, data sensitivity , and analysis easy.
Innovation
- Develop high efficient nonlinear optical coating devices, based on reduced graphene oxide materials
Approach
- Build Z-scan setup Using BBO crystal to test and calibrate the system.
- Graphene Thin Films Collaboration with Dr. Alex at U of A in Little Rock.
- Linear & Nonlinear Optical measurements
- UV-1700 Shimadzu spectrometer, AFM, and Raman Spectroscopy are used to define the sample morphology.
- Measure nonlinear refractive index, thermos optical coefficient, and nonlinear absorption coefficients of Graphene samples with and without gold nanorods.
Key Results
- The value of (β) for nonfunctionalized graphene is around 5.58 *10-2 and 6.42 *10-2 cm/W when deposited with gold nanorods.
- Thermo optical coefficient for NFG was found to be 0.772×10-6 /C while for Au-NFG was 4.04 x 10-4 /C.

Conclusions & Future Work
- Demonstrate amazing nonlinear thermo-optical properties.
- Graphene has potential for broad nonlinear optical applications, such as optical communication, optical limiting, and optical data storage.
- Explain the result and publish NLO experimental data.
- Decorate graphene with gold nanorods, measure the NLO, and understand the physics.
- Decorated graphene with gold particles enhances the NLO properties.
