Investigation of Photodetectors Based on Mechanically Exfoliated Graphene
Student: Wafaa Gebril
Degree: Ph.D., July 2021
Major Professor: Dr. Omar Manasreh
Research Area(s):
Nanoscience & Engineering
Photonics
Background/Relevance
- Rapid growth in photodetector applications in terms of scale and diversity increases the demand for more research attention in this area to overcome the existing limitations.
- Many novel nanostructured materials such as quantum dots and graphene have emerged as promising candidates for high performance optoelectronics. These materials have shown unique size-dependent optical properties comparing with the corresponding bulk materials.
- In this work, photodetectors based on graphene and colloidal nanocrystals were investigated and characterized.
Approach
- PbSe, CdSe and Ag nanocrystals were synthesized using a published wet chemical growth methods.
- Mechanically exfoliated and CVD methods were used to obtain graphene and transform it on Si/SiO2 substrates.
- The prepared nanomaterials were characterized using Optical microscopy and Raman spectroscopy.
- Patterning interdigital devices and single channel device using Standard optical photolithography.
- Depositing the electrodes metals using Electron-beam evaporator.
- Characterizing the fabricated devices using Keithley 4200 SCS.
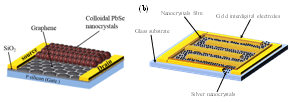
Key Results
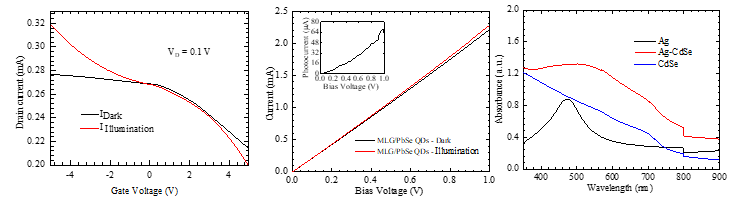
- The transfer curve of the graphene phototransistor shows a photoresponse at negative gate voltages due to the photogating.
- The Ag NP enhanced the absorption in CdSe NC because of the plasmonic effect, as shown in their absorbance spectra.
- PbSe NC increase the photocurrent when used on graphene in graphene photodetector.
Conclusions
- The hybrid graphene/PbSe photodetector demonstrated that the QDs were the light absorber of the device and achieved high responsivity and ditectivity.
- In graphene-based phototransistors, the photogating effect introduced by the p-doped Si/SiO2 substrate was exploited to generate a photoresponse, and the devices showed high and tunable responsivity.
- By adding a Ag NP layer to the CdSe NC a photodetector, an enhancement was obtained in both responsivity and detectivity due to the plasmonic effect of the Ag NPs.
Future Work
- The graphene/PbSe photodetector can be more investigated with different ligands that connect the PbSe NC. Various types of substrates can be investigated in the graphene-based phototransistor.
